Weighing the Benefits and Risks of Semaglutide and Tirzepatide for Weight Loss in People with Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism can make weight loss an uphill battle. Even with strict diets and regular exercise, many people with an underactive thyroid find the scale stubbornly unmoved. But recent advances in medication—specifically GLP-1 receptor agonists like Semaglutide (Ozempic®, Wegovy®) and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro®, Zepbound®)—have shown promising results in helping patients not only lose weight but improve metabolic health overall.
Many hypothyroid patients who previously couldn't lose weight—even with diet and exercise—are now finding success through GLP-1 medications. More energy, better focus, reduced pain, improved blood sugar, and boosted confidence are often reported within months.
Understanding Semaglutide and Tirzepatide
Semaglutide and Tirzepatide belong to a class of medications that mimic incretin hormones, which play a key role in blood sugar regulation and appetite control.
Semaglutide mimics GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1).
Tirzepatide mimics both GLP-1 and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide).
These hormones slow gastric emptying, reduce appetite, and improve insulin sensitivity, making them highly effective for weight management and type 2 diabetes.
Key Data:
A 2021 NEJM study on Semaglutide for weight loss showed a 14.9% average reduction in body weight after 68 weeks.
Tirzepatide trials have shown up to 22.5% weight loss, according to SURMOUNT-1 clinical data.
Both are FDA-approved for obesity treatment (Wegovy®, Zepbound®).
Why It Matters for People With Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism—especially autoimmune types like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis—can cause:
- Slower metabolism
- Increased fat storage
- Insulin resistance
- Fatigue that limits physical activity
These issues often persist even with adequate thyroid hormone replacement (like levothyroxine), making sustainable weight loss difficult.
GLP-1 agonists offer a workaround by reducing caloric intake, lowering insulin resistance, and targeting visceral fat, regardless of thyroid function.
Supporting Fact:
Hypothyroid individuals often exhibit higher TSH and leptin levels, which are associated with increased fat storage and hunger signaling. Medications that act on gut hormones can help break this cycle.
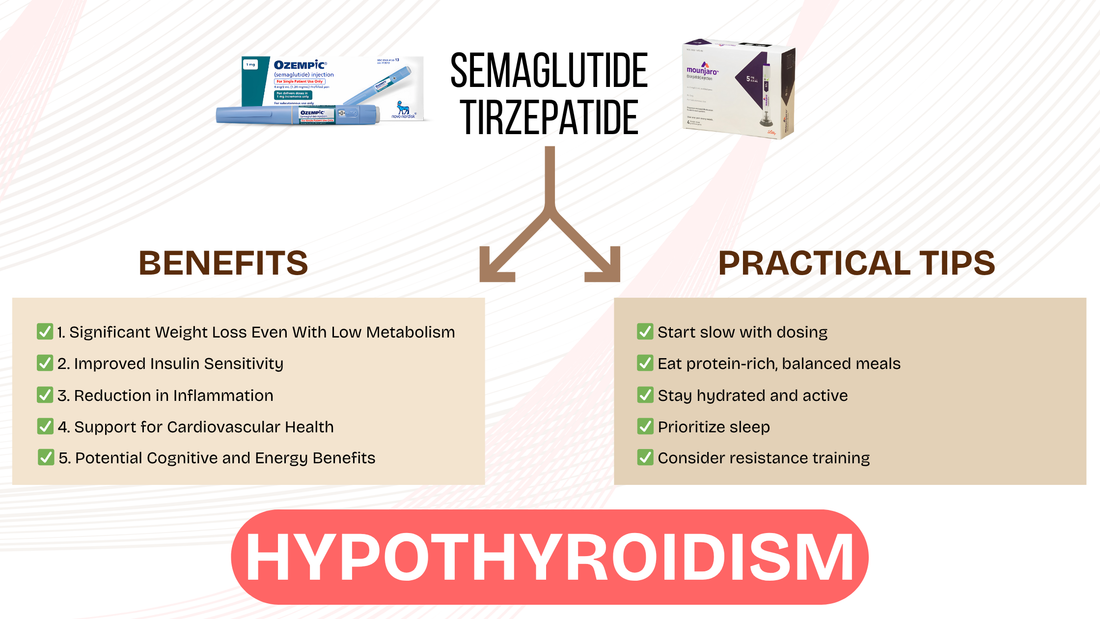
Benefits of Semaglutide or Tirzepatide for Hypothyroid Patients
✅ 1. Enhanced Weight Loss Even With Low Metabolism
These drugs reduce hunger and increase satiety, allowing individuals with low thyroid output to finally lose weight without extreme restriction.
✅ 2. Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Many hypothyroid patients are also insulin resistant—especially those with PCOS or metabolic syndrome. GLP-1 medications lower fasting insulin levels and improve glucose metabolism.
✅ 3. Reduction in Inflammation
Excess weight contributes to chronic inflammation, which can worsen autoimmune thyroid disease. GLP-1 drugs reduce CRP (C-reactive protein), a key inflammation marker.
✅ 4. Support for Cardiovascular Health
People with hypothyroidism have a higher risk of atherosclerosis and high cholesterol. Both Semaglutide and Tirzepatide have shown to lower LDL, total cholesterol, and blood pressure in trials.
✅ 5. Potential Cognitive and Energy Benefits
Many users report improved mental clarity and reduced brain fog, possibly due to better glucose regulation and weight loss, which can reduce fatigue symptoms often seen in hypothyroidism.
Risks and Side Effects to Consider
Common but Often Temporary:
- Nausea
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Fatigue or dizziness
- Loss of appetite
- Less Common:
- Gallstones due to rapid weight loss
- Pancreatitis (rare but serious)
- Hair thinning (can occur with any rapid weight loss, not specific to the medication)
- Thyroid-Specific Concern:
Thyroid C-cell tumors were observed in rodent studies. Thus, contraindicated in people with personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or MEN2 (Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2).
According to the FDA, this risk has not been observed in humans, but precaution is still advised.
The Importance of Monitoring and Active Self-Awareness
It’s crucial to:
Work with a knowledgeable healthcare provider—ideally an endocrinologist or obesity medicine specialist.
Monitor your thyroid levels regularly—as weight loss may reduce your need for levothyroxine.
Be mindful of nutrient deficiencies—especially B12, iron, and selenium, which are important for thyroid function.
Watch for emotional and behavioral shifts—such as loss of interest in eating, food aversions, or body image issues.
Practical Tips for Hypothyroid Patients on GLP-1 Medications
| Strategy | Why It Helps |
|---|---|
| Start slow with dosing | Reduces side effects like nausea |
| Eat protein-rich, balanced meals | Prevents muscle loss and supports metabolism |
| Stay hydrated and active | Improves digestion, preserves energy |
| Prioritize sleep | Essential for hormone regulation |
| Consider resistance training | Helps combat muscle loss and fatigue |
Is It Worth It?
For individuals with hypothyroidism who are struggling with weight gain, low energy, and insulin resistance, Semaglutide or Tirzepatide can be a life-changing adjunct therapy—not a replacement for healthy habits, but a powerful accelerator when used with guidance and intention.
If you're living with hypothyroidism and struggling with weight or metabolic health, medications like Semaglutide or Tirzepatide may be a safe and effective solution—especially when guided by a knowledgeable healthcare provider.
While it's important to be informed about potential side effects, for many patients, the long-term health benefits far outweigh the short-term discomforts.
References:
Wilding JPH et al. "Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity." NEJM, 2021.
Jastreboff AM et al. "Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity." NEJM, 2022.
Garber AJ. "GLP-1 receptor agonists and their effects on weight loss." Endocrine Practice, 2014.
Bianco AC et al. “Management of Hypothyroidism in Adults.” Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2019.